01 Matrix
Problem Description
Given an m x n binary matrix mat, return the distance of the nearest 0 for each cell.
The distance between two adjacent cells is 1.
Examples
Example 1:
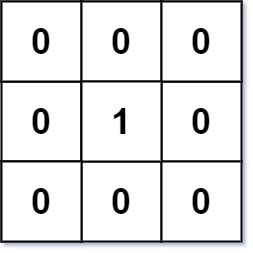
Input: mat = [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,0]]
Output: [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,0]]
Example 2:
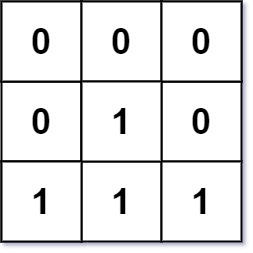
Input: mat = [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[1,1,1]]
Output: [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[1,2,1]]
Constraints
m == mat.lengthn == mat[i].length1 <= m, n <= 10^41 <= m * n <= 10^4mat[i][j] is either 0 or 1.There is at least one 0 in mat.
Solution for 542. 01 Matrix Problem
Approach
-
Initialization:
- Create a queue
qto perform a Breadth-First Search (BFS). - Create a
vismatrix to keep track of visited cells. - Create a
dismatrix to store the distance of each cell from the nearest0.
- Create a queue
-
Enqueue All Zeros:
- Iterate through each cell in the matrix.
- If a cell contains
0, enqueue it with a distance of0and mark it as visited in thevismatrix. - If a cell contains
1, mark it as not visited in thevismatrix.
-
Define Directions:
- Define arrays
drowanddcolto represent the four possible directions (up, right, down, left).
- Define arrays
-
BFS Traversal:
- While the queue is not empty:
- Dequeue the front element.
- For each direction:
- Calculate the new row and column indices.
- Check if the new indices are within the bounds and the cell is not visited.
- If valid, mark the cell as visited, enqueue it with the incremented distance, and update the
dismatrix.
- While the queue is not empty:
-
Return Result:
- After the BFS completes, the
dismatrix contains the required distances.
- After the BFS completes, the
- Solution
Implementation
Live Editor
function Solution(arr) { var updateMatrix = function(mat) { let n = mat.length; let m = mat[0].length; let q = []; let vis = Array.from({ length: n }, () => Array(m).fill(0)); let dis = Array.from({ length: n }, () => Array(m).fill(0)); for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (let j = 0; j < m; j++) { if (mat[i][j] === 0) { q.push([[i, j], 0]); vis[i][j] = 1; } else { vis[i][j] = 0; } } } let drow = [-1, 0, 1, 0]; let dcol = [0, 1, 0, -1]; while (q.length) { let [pos, steps] = q.shift(); let [row, col] = pos; dis[row][col] = steps; for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) { let nrow = row + drow[i]; let ncol = col + dcol[i]; if (nrow >= 0 && ncol >= 0 && nrow < n && ncol < m && vis[nrow][ncol] === 0) { vis[nrow][ncol] = 1; q.push([[nrow, ncol], steps + 1]); } } } return dis; }; const input = [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[1,1,1]] const output = updateMatrix(input) return ( <div> <p> <b>Input: </b> {JSON.stringify(input)} </p> <p> <b>Output:</b> {output.toString()} </p> </div> ); }
Result
Loading...
Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity:
- Space Complexity:
Code in Different Languages
- JavaScript
- Python
- Java
- C++
var updateMatrix = function(mat) {
let n = mat.length;
let m = mat[0].length;
let q = [];
let vis = Array.from({ length: n }, () => Array(m).fill(0));
let dis = Array.from({ length: n }, () => Array(m).fill(0));
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (mat[i][j] === 0) {
q.push([[i, j], 0]);
vis[i][j] = 1;
} else {
vis[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
let drow = [-1, 0, 1, 0];
let dcol = [0, 1, 0, -1];
while (q.length) {
let [pos, steps] = q.shift();
let [row, col] = pos;
dis[row][col] = steps;
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
let nrow = row + drow[i];
let ncol = col + dcol[i];
if (nrow >= 0 && ncol >= 0 && nrow < n && ncol < m && vis[nrow][ncol] === 0) {
vis[nrow][ncol] = 1;
q.push([[nrow, ncol], steps + 1]);
}
}
}
return dis;
};
from collections import deque
class Solution:
def updateMatrix(self, mat):
n = len(mat)
m = len(mat[0])
q = deque()
vis = [[0 for _ in range(m)] for _ in range(n)]
dis = [[0 for _ in range(m)] for _ in range(n)]
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if mat[i][j] == 0:
q.append(((i, j), 0))
vis[i][j] = 1
else:
vis[i][j] = 0
drow = [-1, 0, 1, 0]
dcol = [0, 1, 0, -1]
while q:
(row, col), steps = q.popleft()
dis[row][col] = steps
for i in range(4):
nrow = row + drow[i]
ncol = col + dcol[i]
if 0 <= nrow < n and 0 <= ncol < m and vis[nrow][ncol] == 0:
vis[nrow][ncol] = 1
q.append(((nrow, ncol), steps + 1))
return dis
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class Solution {
public int[][] updateMatrix(int[][] mat) {
int n = mat.length;
int m = mat[0].length;
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
int[][] vis = new int[n][m];
int[][] dis = new int[n][m];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (mat[i][j] == 0) {
q.add(new int[]{i, j, 0});
vis[i][j] = 1;
} else {
vis[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
int[] drow = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
int[] dcol = {0, 1, 0, -1};
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] current = q.poll();
int row = current[0];
int col = current[1];
int steps = current[2];
dis[row][col] = steps;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nrow = row + drow[i];
int ncol = col + dcol[i];
if (nrow >= 0 && ncol >= 0 && nrow < n && ncol < m && vis[nrow][ncol] == 0) {
vis[nrow][ncol] = 1;
q.add(new int[]{nrow, ncol, steps + 1});
}
}
}
return dis;
}
}
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> updateMatrix(vector<vector<int>>& mat) {
int n = mat.size();
int m = mat[0].size();
queue<pair<pair<int, int>, int>> q;
vector<vector<int>> vis(n, vector<int>(m, 0));
vector<vector<int>> dis(n, vector<int>(m, 0));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (mat[i][j] == 0) {
q.push({{i, j}, 0});
vis[i][j] = 1;
} else {
vis[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
int drow[] = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
int dcol[] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
while (!q.empty()) {
int row = q.front().first.first;
int col = q.front().first.second;
int steps = q.front().second;
q.pop();
dis[row][col] = steps;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nrow = row + drow[i];
int ncol = col + dcol[i];
if (nrow >= 0 && ncol >= 0 && nrow < n && ncol < m && vis[nrow][ncol] == 0) {
vis[nrow][ncol] = 1;
q.push({{nrow, ncol}, steps + 1});
}
}
}
return dis;
}
};
References
-
LeetCode Problem: 542. 01 Matrix
-
Solution Link: LeetCode Solution