Diameter of Binary tree
Problem Description
Given the root of a binary tree, return the length of the diameter of the tree.
The diameter of a binary tree is the length of the longest path between any two nodes in a tree. This path may or may not pass through the root.
The length of a path between two nodes is represented by the number of edges between them.
Examples
Example 1:
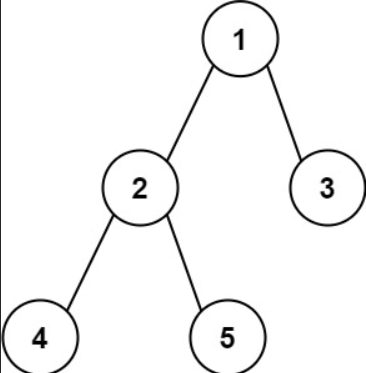
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: 3
Explanataion: 3 is the length of the path [4,2,1,3] or [5,2,1,3].
Example 2:
Input: root = [1,2]
Output: 1
Constraints
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 10^4]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Solution for Diameter of Binary tree
Approach
Brute Force
- Define a Helper Function:
- Create a function to calculate the height of a tree.
- Calculate Diameter:
- For each node, calculate the diameter passing through that node.
- The diameter passing through a node is the sum of the heights of its left and right subtrees.
- Compare this diameter with the global maximum diameter.
- Traverse Tree:
- Perform a traversal of the tree (e.g., in-order, pre-order) to compute the diameter for each node.
Implementation:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
};
int height(TreeNode* node) {
if (node == NULL) {
return 0;
}
return 1 + max(height(node->left), height(node->right));
}
int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) {
return 0;
}
// Get the height of left and right sub-trees
int left_height = height(root->left);
int right_height = height(root->right);
// Get the diameter of left and right sub-trees
int left_diameter = diameterOfBinaryTree(root->left);
int right_diameter = diameterOfBinaryTree(root->right);
// Calculate diameter passing through the root
return max(left_height + right_height, max(left_diameter, right_diameter));
}
int main() {
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(1);
root->left = new TreeNode(2);
root->right = new TreeNode(3);
root->left->left = new TreeNode(4);
root->left->right = new TreeNode(5);
cout << "Diameter of the binary tree is: " << diameterOfBinaryTree(root) << endl;
return 0;
}
Complexity:
- Time Complexity:
O(n^2)because for each node, we are calculating the height which takes O(n) time. - Space Complexity:
O(n)due to the recursion stack.
Corner Cases:
- Empty tree: Should return
0. - Single node tree: Should return
0as there are no edges.
Optimized Approach
- Define a Helper Function::
- Create a function to calculate both the height and the diameter of the tree simultaneously.
- Single Traversal:
- Traverse the tree once, calculating the height and updating the maximum diameter at each node.
Implementation:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
int diameter;
int height(TreeNode* node) {
if (node == NULL) {
return 0;
}
int left_height = height(node->left);
int right_height = height(node->right);
// Update the diameter if left_height + right_height is larger
diameter = max(diameter, left_height + right_height);
// Height of the current node is max of heights of left and right subtrees plus 1
return 1 + max(left_height, right_height);
}
int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode* root) {
diameter = 0;
height(root);
return diameter;
}
};
int main() {
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(1);
root->left = new TreeNode(2);
root->right = new TreeNode(3);
root->left->left = new TreeNode(4);
root->left->right = new TreeNode(5);
Solution solution;
cout << "Diameter of the binary tree is: " << solution.diameterOfBinaryTree(root) << endl;
return 0;
}
Complexity:
- Time Complexity:
O(n)since we are traversing each node only once. - Space Complexity:
O(n)due to the recursion stack.
Corner Cases:
-
Empty tree: Should return
0. -
Single node tree: Should return
0as there are no edges.Code in Different Languages
- JavaScript
- TypeScript
- Python
- Java
- C++
var diameterOfBinaryTree = function(root) {
let diameter = 0;
function height(node) {
if (node === null) return 0;
let leftHeight = height(node.left);
let rightHeight = height(node.right);
// Update the diameter
diameter = Math.max(diameter, leftHeight + rightHeight);
return 1 + Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight);
}
height(root);
return diameter;
};
function diameterOfBinaryTree(root: TreeNode | null): number {
let diameter = 0;
function height(node: TreeNode | null): number {
if (node === null) return 0;
let leftHeight = height(node.left);
let rightHeight = height(node.right);
// Update the diameter
diameter = Math.max(diameter, leftHeight + rightHeight);
return 1 + Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight);
}
height(root);
return diameter;
}
class Solution(object):
def diameterOfBinaryTree(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
self.diameter = 0
def height(node: TreeNode) -> int:
if not node:
return 0
left_height = height(node.left)
right_height = height(node.right)
# Update the diameter
self.diameter = max(self.diameter, left_height + right_height)
return 1 + max(left_height, right_height)
height(root)
return self.diameter
import java.util.Arrays;
class Solution {
private int diameter;
public int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
diameter = 0;
height(root);
return diameter;
}
private int height(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftHeight = height(node.left);
int rightHeight = height(node.right);
// Update the diameter
diameter = Math.max(diameter, leftHeight + rightHeight);
return 1 + Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight);
}
};
class Solution {
public:
int diameter;
int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode* root) {
diameter = 0;
height(root);
return diameter;
}
private:
int height(TreeNode* node) {
if (node == nullptr) {
return 0;
}
int leftHeight = height(node->left);
int rightHeight = height(node->right);
// Update the diameter
diameter = max(diameter, leftHeight + rightHeight);
return 1 + max(leftHeight, rightHeight);
}
};
References
-
LeetCode Problem: Diameter of Binary tree
-
Solution Link: LeetCode Solution