Symmetric Tree Solution
Problem Description
Given the root of a binary tree, check whether it is a mirror of itself (i.e., symmetric around its center).
Examples
Example 1:
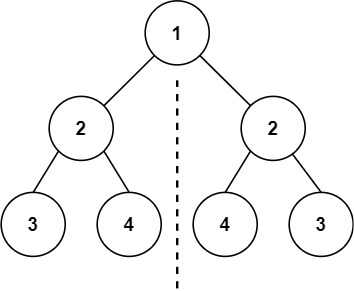
Input: root = [1,2,2,3,4,4,3]
Output: true
Example 2:
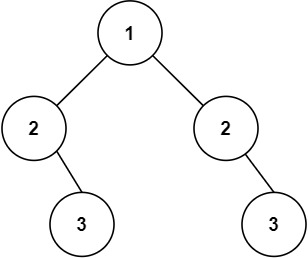
Input: root = [1,2,2,null,3,null,3]
Output: false
Constraints
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 1000]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Solution for Symmetric Tree Problem
Intuition And Approach
To check if a binary tree is symmetric, we need to compare its left subtree and right subtree. We can define a recursive helper function that takes two nodes as input, one from the left subtree and one from the right subtree. The helper function returns true if both nodes are null, or if their values are equal and their subtrees are symmetric.
- Recursive
- Non-recursive
Approach 1 : Recursive
- Define a recursive helper function
isMirror(node1, node2)that returns true if both nodes are null or if their values are equal and their subtrees are symmetric. - Start the recursion from the root of the tree using
isMirror(root.left, root.right). - Return the result of the recursive check.
Code in Different Languages
- Java
- Python
- C++
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
return root == null || isSymmetricHelp(root.left, root.right);
}
private boolean isSymmetricHelp(TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
if (left == null || right == null)
return left == right;
if (left.val != right.val)
return false;
return isSymmetricHelp(left.left, right.right) && isSymmetricHelp(left.right, right.left);
}
def isSymmetric(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:
if root is None:
return True
def isSymmetricHelp(left, right):
if left is None or right is None:
return left == right
if left.val != right.val:
return False
return isSymmetricHelp(left.left, right.right) and isSymmetricHelp(left.right, right.left)
return isSymmetricHelp(root.left, root.right)
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return true;
}
return isSymmetricHelp(root->left, root->right);
}
bool isSymmetricHelp(TreeNode* left, TreeNode* right) {
if (left == nullptr || right == nullptr)
return left == right;
if (left->val != right->val)
return false;
return isSymmetricHelp(left->left, right->right) && isSymmetricHelp(left->right, right->left);
}
Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity: O(n) where n is the number of nodes in the binary tree.
- Space Complexity: O(h) where h is the height of the binary tree.
Approach 2 : Non-Recursive (Stack-based)
- If the root is null, return true as an empty tree is symmetric.
- Initialize a stack to store nodes for comparison.
- If the root's left child is not null, check if the root's right child is also not null. If either is null while the other is not, return false.
- Push both the left and right children of the root onto the stack.
- While the stack is not empty:
- If the size of the stack is odd, return false as nodes should be in pairs.
- Pop two nodes from the stack. These nodes should be symmetric.
- Compare their values. If they are not equal, return false.
- For each popped pair of nodes, push their left and right children in the symmetric order onto the stack:
- Push the left child of the left node and the right child of the right node.
- Push the right child of the left node and the left child of the right node.
- If one node has a child while the other does not, return false.
- If all nodes are processed without mismatch, return true as the tree is symmetric.
Code in Different Languages
- Java
- Python
- C++
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return true;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode left, right;
if (root.left != null) {
if (root.right == null)
return false;
stack.push(root.left);
stack.push(root.right);
} else if (root.right != null) {
return false;
}
while (!stack.empty()) {
if (stack.size() % 2 != 0)
return false;
right = stack.pop();
left = stack.pop();
if (right.val != left.val)
return false;
if (left.left != null) {
if (right.right == null)
return false;
stack.push(left.left);
stack.push(right.right);
} else if (right.right != null) {
return false;
}
if (left.right != null) {
if (right.left == null)
return false;
stack.push(left.right);
stack.push(right.left);
} else if (right.left != null) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
def isSymmetric(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:
if root is None:
return True
stack = []
left, right = None, None
if root.left is not None:
if root.right is None:
return False
stack.append(root.left)
stack.append(root.right)
elif root.right is not None:
return False
while stack:
if len(stack) % 2 != 0:
return False
right = stack.pop()
left = stack.pop()
if right.val != left.val:
return False
if left.left is not None:
if right.right is None:
return False
stack.append(left.left)
stack.append(right.right)
elif right.right is not None:
return False
if left.right is not None:
if right.left is None:
return False
stack.append(left.right)
stack.append(right.left)
elif right.left is not None:
return False
return True
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return true;
}
stack<TreeNode*> stack;
TreeNode *left, *right;
if (root->left != nullptr) {
if (root->right == nullptr)
return false;
stack.push(root->left);
stack.push(root->right);
} else if (root->right != nullptr) {
return false;
}
while (!stack.empty()) {
if (stack.size() % 2 != 0)
return false;
right = stack.top();
stack.pop();
left = stack.top();
stack.pop();
if (right->val != left->val)
return false;
if (left->left != nullptr) {
if (right->right == nullptr)
return false;
stack.push(left->left);
stack.push(right->right);
} else if (right->right != nullptr) {
return false;
}
if (left->right != nullptr) {
if (right->left == nullptr)
return false;
stack.push(left->right);
stack.push(right->left);
} else if (right->left != nullptr) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity: O(n) where n is the number of nodes in the binary tree.
- Space Complexity: O(n) in the worst case due to the stack.
References
- LeetCode Problem: Symmetric Tree Problem
- Solution Link: Symmetric Tree Solution on LeetCode
- Authors GeeksforGeeks Profile: Vipul lakum