Populating Next Right Pointer To Each Node II
Problem Description
Given the root of a binary tree and an integer targetSum, return all root-to-leaf paths where the sum of the node values in the path equals targetSum. Each path should be returned as a list of node values, and paths are represented as lists of node values.
Examples
Example 1:
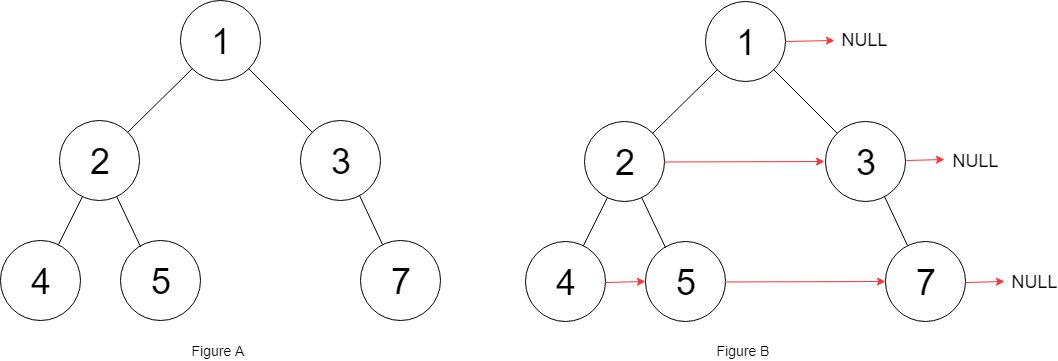
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,null,7]
Output: [1,#,2,3,#,4,5,7,#]
Example 2:
Input: root = []
Output: []
Constraints
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 6000].
Solution for Binary Tree Problem
Intuition And Approach
To find all root-to-leaf paths where the sum equals targetSum, we can use Depth-First Search (DFS). We'll traverse the tree and keep track of the current path and its sum. When a leaf node is reached, we check if the current path's sum equals targetSum. If it does, we add the path to our result list.
- Recursive
Code in Different Languages
- Java
- Python
- C++
private void dfs(TreeNode node, int sum, List<Integer> path, List<List<Integer>> result) { if (node == null) return; path.add(node.val); if (node.left == null && node.right == null && node.val == sum) { result.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); } else { dfs(node.left, sum - node.val, path, result); dfs(node.right, sum - node.val, path, result); } path.remove(path.size() - 1); }
class Solution: def pathSum(self, root: TreeNode, targetSum: int) -> List[List[int]]: def dfs(node, current_path, current_sum): if not node: return current_path.append(node.val) current_sum += node.val if not node.left and not node.right and current_sum == targetSum: result.append(list(current_path)) else: dfs(node.left, current_path, current_sum) dfs(node.right, current_path, current_sum) current_path.pop()
void dfs(TreeNode* node, int sum, vector<int>& path, vector<vector<int>>& result) { if (!node) return; path.push_back(node->val); if (!node->left && !node->right && node->val == sum) { result.push_back(path); } else { dfs(node->left, sum - node->val, path, result); dfs(node->right, sum - node->val, path, result); } path.pop_back(); }
Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity: where n is the number of nodes in the binary tree.
- Space Complexity: where h is the height of the binary tree.