Search in a Binary Search Tree
Problem Description
You are given the root of a binary search tree (BST) and an integer val.
Find the node in the BST that the node's value equals val and return the subtree rooted with that node. If such a node does not exist, return null.
Examples
Example 1:
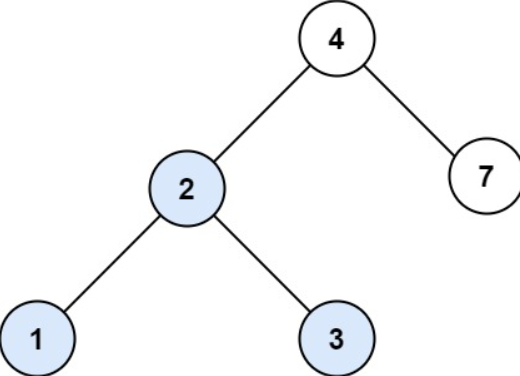
Input: root = [4,2,7,1,3], val = 2
Output: [2,1,3]
Example 2:
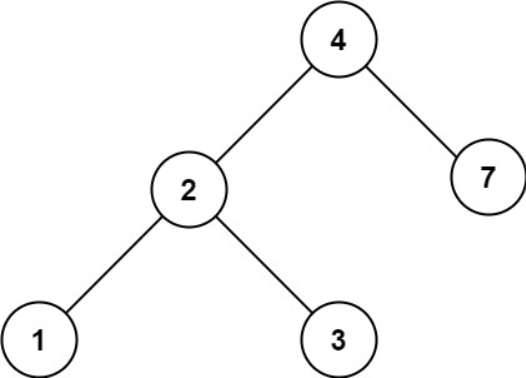
Input: root = [4,2,7,1,3], val = 5
Output: []
Constraints
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 5000]. 1 <= Node.val <= 10^7rootis a binary search tree.1 <= val <= 10^7
Solution for Search in a Binary Search Tree
Approach
Brute Force
- Traverse the Tree: Perform a level-order or in-order traversal of the tree.
- Compare Values: At each node, compare its value with the given value
val. - Return Subtree: If the node’s value equals
val, return the subtree rooted at that node. - Return Null: If the traversal completes without finding the node, return
null.
Implementation:
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
def findNode(root, val):
if root is None:
return None
queue = [root]
while queue:
node = queue.pop(0)
if node.val == val:
return node
if node.left:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
return None
# Example usage
root = TreeNode(4, TreeNode(2, TreeNode(1), TreeNode(3)), TreeNode(7))
val = 2
subtree = findNode(root, val)
print(subtree.val if subtree else "Node not found")
Complexity:
- Time Complexity:
O(n)- We might have to visit every node in the tree. - Space Complexity:
O(n)- In the worst case, the queue can hold all nodes in the tree (for level-order traversal).
Corner Cases:
- Empty tree: Should return
null. - Value not found: Should return
null.
Optimized Approach
- Leverage BST Properties: Use the properties of the BST (left subtree contains nodes with values less than the root, and the right subtree contains nodes with values greater than the root).
- Binary Search: Traverse the tree using a binary search-like approach:
- If
valis less than the current node’s value, move to the left child. - If
valis greater than the current node’s value, move to the right child. - If
valequals the current node’s value, return the current node.
- If
- Return Null: If a leaf node is reached without finding the value, return
null.
Implementation:
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
def findNode(root, val):
current = root
while current:
if current.val == val:
return current
elif val < current.val:
current = current.left
else:
current = current.right
return None
# Example usage
root = TreeNode(4, TreeNode(2, TreeNode(1), TreeNode(3)), TreeNode(7))
val = 2
subtree = findNode(root, val)
print(subtree.val if subtree else "Node not found")
Complexity:
- Time Complexity:
O(h)-his the height of the tree. In the worst case, it can be O(n) for a skewed tree, but in a balanced tree, it is O(log n). - Space Complexity:
O(1)- We are not using any extra space except for the input and output.
Corner Cases:
-
Empty tree: Should return
null. -
Value not found: Should return
null. -
Single node tree: If the single node does not match
val, should returnnull.Code in Different Languages
- JavaScript
- TypeScript
- Python
- Java
- C++
var searchBST = function(root, val) {
if (root === null) {
return null;
} else {
if (root.val === val) {
return root;
} else if (root.val < val) {
return searchBST(root.right, val);
} else {
return searchBST(root.left, val);
}
}
};
function searchBST(root: TreeNode | null, val: number): TreeNode | null {
if (root === null) {
return null;
} else {
if (root.val === val) {
return root;
} else if (root.val < val) {
return searchBST(root.right, val);
} else {
return searchBST(root.left, val);
}
}
}
class Solution(object):
def searchBST(self, root, val):
if root is None:
return None
else:
if root.val == val:
return root
elif root.val < val:
return self.searchBST(root.right, val)
else:
return self.searchBST(root.left, val)
import java.util.Arrays;
class Solution {
public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
} else {
if (root.val == val) {
return root;
} else if (root.val < val) {
return searchBST(root.right, val);
} else {
return searchBST(root.left, val);
}
}
}
}
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* searchBST(TreeNode* root, int val) {
if(root==NULL){
return NULL;
}
else{
if(root->val == val){
return root;
}else if(root->val < val){
return searchBST(root->right,val);
}else{
return searchBST(root->left,val);
}
return NULL;
}
return NULL;
}
};
References
-
LeetCode Problem: Search in a Binary Search Tree
-
Solution Link: LeetCode Solution