Diagonal Traverse II
Problem Description
Given a 2D integer array nums, return all elements of nums in diagonal order as shown in the below images.
Examples
Example 1:
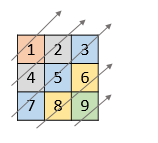
Input: nums = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
Output: [1,4,2,7,5,3,8,6,9]
Example 2:
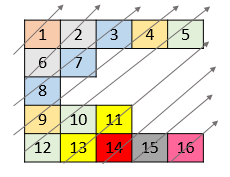
Input: nums = [[1,2,3,4,5],[6,7],[8],[9,10,11],[12,13,14,15,16]]
Output: [1,6,2,8,7,3,9,4,12,10,5,13,11,14,15,16]
Constraints
1 <= nums.length <= 10^51 <= nums[i].length <= 10^51 <= sum(nums[i].length) <= 10^51 <= nums[i][j] <= 10^5
Solution for Diagonal Traverse II Problem
Approach
The problem requires traversing the 2D list in a diagonal manner. Diagonal order means we visit all elements of each diagonal, starting from the top-left element (0, 0). The diagonals can be visualized as lines of elements where the sum of the row index and column index is constant.
Steps to Solve
-
Initialize a Queue and Visited Matrix:
- Use a queue to facilitate breadth-first traversal starting from the top-left element.
- Use a
visitedmatrix to keep track of visited elements to avoid processing the same element multiple times.
-
Determine Dimensions:
- Determine the maximum number of columns (
n) by iterating through each row of the input list. - The number of rows (
m) is simply the length of the input list.
- Determine the maximum number of columns (
-
Breadth-First Traversal:
- Start from
(0, 0), mark it as visited, and add it to the queue. - While the queue is not empty, perform the following steps:
- Dequeue the front element (current position).
- Add the value at the current position to the result list.
- Check and enqueue the element directly below the current position if it exists and has not been visited.
- Check and enqueue the element to the right of the current position if it exists and has not been visited.
- Start from
-
Return the Result:
- After processing all elements in the queue, the result list will contain the elements in diagonal order.
- Solution
Implementation
Live Editor
function Solution(arr) { function findDiagonalOrder(nums) { let ans = []; let q = []; let vis = nums.map(row => row.map(() => false)); let m = nums.length; let n = 0; for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) { if (nums[i].length > n) { n = nums[i].length; } } q.push([0, 0]); vis[0][0] = true; while (q.length > 0) { let [row, col] = q.shift(); ans.push(nums[row][col]); if (row + 1 < m && col < nums[row + 1].length && !vis[row + 1][col]) { q.push([row + 1, col]); vis[row + 1][col] = true; } if (row < m && col + 1 < nums[row].length && !vis[row][col + 1]) { q.push([row, col + 1]); vis[row][col + 1] = true; } } return ans; } const input = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]] const output = findDiagonalOrder(input) return ( <div> <p> <b>Input: </b> {JSON.stringify(input)} </p> <p> <b>Output:</b> {output.toString()} </p> </div> ); }
Result
Loading...
Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity:
- Space Complexity:
Code in Different Languages
- JavaScript
- TypeScript
- Python
- Java
- C++
findDiagonalOrder(nums) {
let ans = [];
let q = [];
let vis = nums.map(row => row.map(() => false));
let m = nums.length;
let n = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
if (nums[i].length > n) {
n = nums[i].length;
}
}
q.push([0, 0]);
vis[0][0] = true;
while (q.length > 0) {
let [row, col] = q.shift();
ans.push(nums[row][col]);
if (row + 1 < m && col < nums[row + 1].length && !vis[row + 1][col]) {
q.push([row + 1, col]);
vis[row + 1][col] = true;
}
if (row < m && col + 1 < nums[row].length && !vis[row][col + 1]) {
q.push([row, col + 1]);
vis[row][col + 1] = true;
}
}
return ans;
}
class Solution {
findDiagonalOrder(nums: number[][]): number[] {
let ans: number[] = [];
let q: [number, number][] = [];
let vis: boolean[][] = nums.map(row => row.map(() => false));
let m = nums.length;
let n = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
if (nums[i].length > n) {
n = nums[i].length;
}
}
q.push([0, 0]);
vis[0][0] = true;
while (q.length > 0) {
let [row, col] = q.shift();
ans.push(nums[row][col]);
if (row + 1 < m && col < nums[row + 1].length && !vis[row + 1][col]) {
q.push([row + 1, col]);
vis[row + 1][col] = true;
}
if (row < m && col + 1 < nums[row].length && !vis[row][col + 1]) {
q.push([row, col + 1]);
vis[row][col + 1] = true;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
from collections import deque
class Solution:
def findDiagonalOrder(self, nums):
ans = []
q = deque()
vis = [[False] * len(row) for row in nums]
m = len(nums)
n = 0
for i in range(m):
if len(nums[i]) > n:
n = len(nums[i])
q.append((0, 0))
vis[0][0] = True
while q:
row, col = q.popleft()
ans.append(nums[row][col])
if row + 1 < m and col < len(nums[row + 1]) and not vis[row + 1][col]:
q.append((row + 1, col))
vis[row + 1][col] = True
if row < m and col + 1 < len(nums[row]) and not vis[row][col + 1]:
q.append((row, col + 1))
vis[row][col + 1] = True
return ans
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public List<Integer> findDiagonalOrder(List<List<Integer>> nums) {
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
boolean[][] vis = new boolean[nums.size()][];
int m = nums.size();
int n = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
if (nums.get(i).size() > n) {
n = nums.get(i).size();
}
vis[i] = new boolean[nums.get(i).size()];
}
q.offer(new int[]{0, 0});
vis[0][0] = true;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] el = q.poll();
int row = el[0];
int col = el[1];
ans.add(nums.get(row).get(col));
if (row + 1 < m && col < nums.get(row + 1).size() && !vis[row + 1][col]) {
q.offer(new int[]{row + 1, col});
vis[row + 1][col] = true;
}
if (row < m && col + 1 < nums.get(row).size() && !vis[row][col + 1]) {
q.offer(new int[]{row, col + 1});
vis[row][col + 1] = true;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findDiagonalOrder(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {
vector<int> ans;
queue<pair<int,int>> q;
vector<vector<int>> vis = nums;
int m = nums.size();
int n = 0;
for(int i=0 ; i<m ; i++){
if(nums[i].size()>n){
n = nums[i].size();
}
}
q.push({0,0});
vis[0][0] = -1;
while(!q.empty()){
auto el = q.front();
int row = el.first;
int col = el.second;
q.pop();
ans.push_back(nums[row][col]);
if(row+1<m && col < nums[row+1].size() && vis[row+1][col]!=-1){
q.push({row+1,col});
vis[row+1][col] = -1;
}
if(row<m && col+1 < nums[row].size() && vis[row][col+1]!=-1){
q.push({row,col+1});
vis[row][col+1] = -1;
}
}
return ans;
}
};
References
-
LeetCode Problem: 1424. Diagonal Traverse II
-
Solution Link: LeetCode Solution