Flatten a Multilevel Doubly Linked List
Problem Description
You are given a doubly linked list, which contains nodes that have a next pointer, a previous pointer, and an additional child pointer. This child pointer may or may not point to a separate doubly linked list, also containing these special nodes. These child lists may have one or more children of their own, and so on, to produce a multilevel data structure as shown in the example below.
Given the head of the first level of the list, flatten the list so that all the nodes appear in a single-level, doubly linked list. Let curr be a node with a child list. The nodes in the child list should appear after curr and before curr.next in the flattened list.
Return the head of the flattened list. The nodes in the list must have all of their child pointers set to null.
Examples
Example 1:
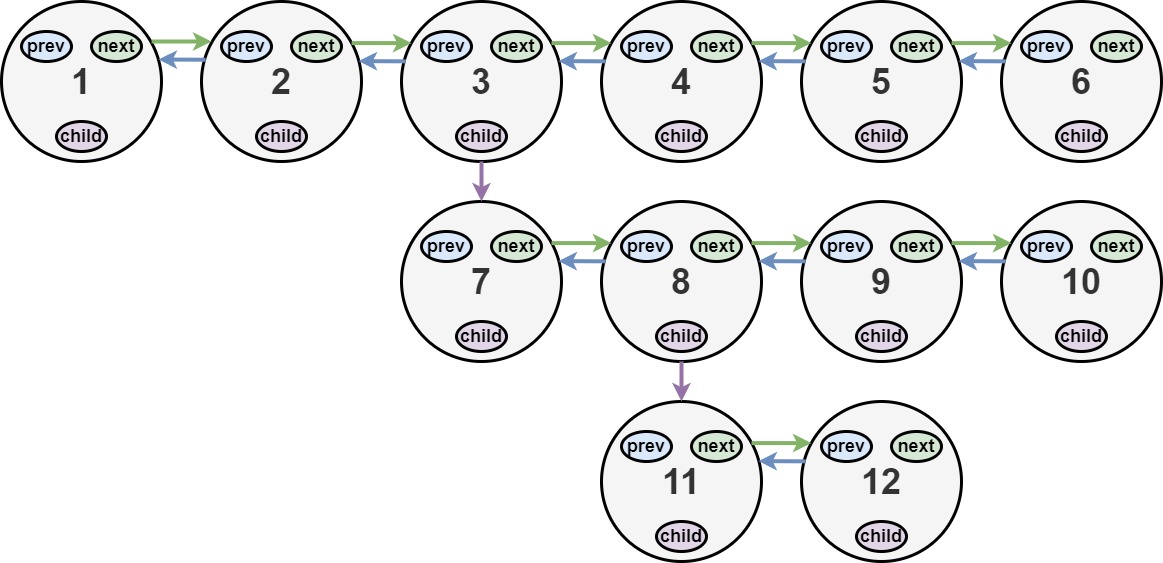
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5,6,null,null,null,7,8,9,10,null,null,11,12]
Output: [1,2,3,7,8,11,12,9,10,4,5,6]
Explanation: The multilevel linked list in the input is shown.
After flattening the multilevel linked list it becomes:
 Example 2:
Example 2:
Input: head = [1,2,null,3]
Output: [1,3,2]
Explanation: The multilevel linked list in the input is shown.
Example 3:
Input: head = []
Output: []
Explanation: There could be empty list in the input.
Constraints
- The number of Nodes will not exceed 1000.
1 <= Node.val <= 10^5
Solution for Flatten a Multilevel Doubly Linked List
Approach
- Recursively traverse the original linked list, pushing nodes into a vector in the order they are visited, considering child nodes first.
- Construct a flattened linked list from this vector, ensuring proper connections between nodes.
- Solution
Implementation
function Node(val, prev = null, next = null, child = null) { return { val: val, prev: prev, next: next, child: child }; } function flatten(head) { if (!head) return null; let stack = [head]; let dummy = new Node(0); let prev = dummy; while (stack.length > 0) { let current = stack.pop(); if (current.next) stack.push(current.next); if (current.child) { stack.push(current.child); current.child = null; } prev.next = current; current.prev = prev; prev = current; } dummy.next.prev = null; return dummy.next; } const input = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, null, null, null, 7, 8, 9, 10, null, null, 11, 12]; // Construct the linked list from the input array let head = new Node(input[0]); let current = head; let stack = [head]; for (let i = 1; i < input.length; i++) { if (input[i] === null) continue; let newNode = new Node(input[i]); current.next = newNode; newNode.prev = current; current = newNode; if (input[i] !== null) { stack.push(current); } } // Link child nodes for (let i = 0; i < input.length; i++) { if (input[i] === null) { let parent = stack.pop(); parent.child = parent.next; parent.next = null; if (parent.child) parent.child.prev = null; } } // Flatten the linked list let output = flatten(head); return ( <div> <p> <b>Input: </b>{JSON.stringify(input)} </p> <p> <b>Output:</b> {output ? output.toString() : 'null'} </p> </div> );
Code in Different Languages
- JavaScript
- TypeScript
- Python
- Java
- C++
var flatten = function(head) {
const arr = [];
const helper = (node) => {
if(!node) return;
arr.push(node);
helper(node.child);
helper(node.next);
};
helper(head);
for(let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i].prev = arr[i-1] || null;
arr[i].next = arr[i+1] || null;
arr[i].child = null;
}
return arr[0] || null;
};
function flatten(head: Node | null): Node | null {
if (!head) return null;
let pseudoHead: Node = new Node(0);
flattenDFS(pseudoHead, head);
pseudoHead.next.prev = null;
return pseudoHead.next;
};
function flattenDFS(prev: Node, curr: Node | null): Node | null {
if (!curr) return prev;
// Connect nodes
curr.prev = prev;
prev.next = curr;
let tempNext: Node | null = curr.next;
let tail = flattenDFS(curr, curr.child);
// Clean child
curr.child = null;
return flattenDFS(tail, tempNext);
}
class Solution:
def flatten(self, head: 'Node') -> 'Node':
def getTail(node):
prev = None
while node:
_next = node.next
if node.child:
# ... <-> node <-> node.child <-> ...
node.next = node.child
node.child = None
node.next.prev = node
# get the end node of the node.child list
prev = getTail(node.next)
if _next:
# ... <-> prev (end node) <-> _next (originally node.next) <-> ...
_next.prev = prev
prev.next = _next
else:
prev = node
node = _next # loop through the list of nodes
return prev # return end node
getTail(head)
return head
class Solution {
Node prev = null;
public Node flatten(Node head) {
dfsHelper(head);
return head;
}
public void dfsHelper(Node current) {
if (current == null) return;
// postorder traversal, going right first or next in this case
dfsHelper(current.next);
dfsHelper(current.child);
// don't forget to set prev.prev pointer
if (prev != null) prev.prev = current;
// see explanation below
current.next = prev;
current.child = null;
prev = current;
}
}
class Node {
public:
int val;
Node* prev;
Node* next;
Node* child;
};
void solve(Node *head, vector<Node*>& ans, Node *curr) {
if (curr == NULL) {
return;
}
ans.push_back(curr);
if (curr->child) {
solve(head, ans, curr->child);
}
if (curr->next) {
solve(head, ans, curr->next);
}
}
Node* flatten(Node* head) {
if (!head) return nullptr;
vector<Node*> ans;
Node *curr = head;
solve(head, ans, curr);
Node *newHead = NULL;
curr = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < ans.size(); i++) {
if (curr == NULL) {
curr = ans[i];
newHead = ans[i];
} else {
curr->next = ans[i];
curr->next->prev = curr;
curr->child = NULL;
curr = curr->next;
}
}
return newHead;
}
Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity:
- Space Complexity:
References
-
LeetCode Problem: Count Primes
-
Solution Link: LeetCode Solution
