Naive Pattern Matching Algorithm (Geeks for Geeks)
1. What is the Naive Pattern Matching Algorithm?
The Naive Pattern Matching algorithm is a straightforward approach for finding occurrences of a pattern string within a text string. It compares the pattern to each substring of the text and checks for a match.
2. Algorithm for Naive Pattern Matching
- Loop through the text, and for each position in the text, check if the pattern matches the substring starting at that position.
- If a match is found, record the starting index of the match.
3. How does the Naive Pattern Matching Algorithm work?
- For each position in the text, compare the substring of the text starting at that position with the pattern.
- If the pattern matches the substring, record the starting index.
- Continue this process until the end of the text is reached.
4. Problem Description
Given a text string and a pattern string, implement the Naive Pattern Matching algorithm to find all occurrences of the pattern in the text.
5. Examples
Example 1:
Input: text = "THIS IS A TEST TEXT", pattern = "TEST"
Output: Pattern found at index 10
Example 2:
Input: text = "AABAACAADAABAABA", pattern = "AABA"
Output: Pattern found at index 0, Pattern found at index 9, Pattern found at index 12
Explanation of Example 1:
- The pattern "TEST" is found in the text "THIS IS A TEST TEXT" at index 10.
Visual Example
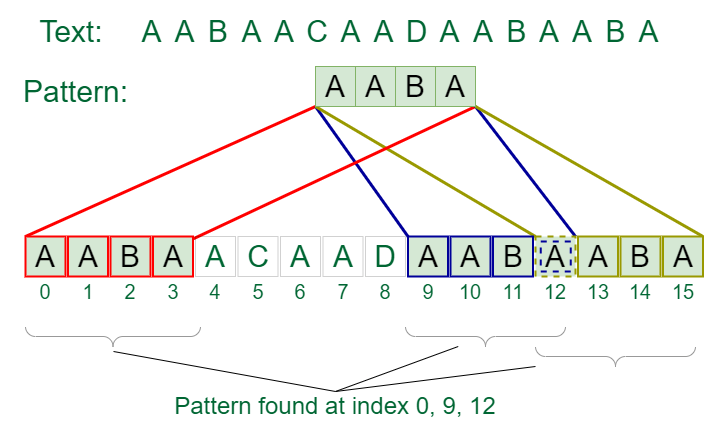
6. Constraints
- The text and pattern can contain any number of characters.
- All characters are characters.
7. Implementation
- Python
- C++
- Java
- JavaScript
def naive_pattern_search(text, pattern):
n = len(text)
m = len(pattern)
for i in range(n - m + 1):
j = 0
while j < m and text[i + j] == pattern[j]:
j += 1
if j == m:
print(f"Pattern found at index {i}")
# Example usage
text = "THIS IS A TEST TEXT"
pattern = "TEST"
naive_pattern_search(text, pattern)
text = "AABAACAADAABAABA"
pattern = "AABA"
naive_pattern_search(text, pattern)
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void naivePatternSearch(string txt, string pat) {
int n = txt.size();
int m = pat.size();
for (int i = 0; i <= n - m; i++) {
int j;
for (j = 0; j < m; j++)
if (txt[i + j] != pat[j])
break;
if (j == m)
cout << "Pattern found at index " << i << endl;
}
}
int main() {
string txt = "THIS IS A TEST TEXT";
string pat = "TEST";
naivePatternSearch(txt, pat);
txt = "AABAACAADAABAABA";
pat = "AABA";
naivePatternSearch(txt, pat);
return 0;
}
public class NaivePatternMatching {
static void naivePatternSearch(String txt, String pat) {
int n = txt.length();
int m = pat.length();
for (int i = 0; i <= n - m; i++) {
int j;
for (j = 0; j < m; j++)
if (txt.charAt(i + j) != pat.charAt(j))
break;
if (j == m)
System.out.println("Pattern found at index " + i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String txt = "THIS IS A TEST TEXT";
String pat = "TEST";
naivePatternSearch(txt, pat);
txt = "AABAACAADAABAABA";
pat = "AABA";
naivePatternSearch(txt, pat);
}
}
function naivePatternSearch(txt, pat) {
const n = txt.length;
const m = pat.length;
for (let i = 0; i <= n - m; i++) {
let j;
for (j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (txt[i + j] !== pat[j]) {
break;
}
}
if (j === m) {
console.log(`Pattern found at index ${i}`);
}
}
}
// Example usage:
let text = "THIS IS A TEST TEXT";
let pattern = "TEST";
naivePatternSearch(text, pattern);
text = "AABAACAADAABAABA";
pattern = "AABA";
naivePatternSearch(text, pattern);
8. Complexity Analysis
-
Time Complexity:
- Worst-case: , where is the length of the text and is the length of the pattern.
- Best-case: when all characters of the pattern are different.
-
Space Complexity: as it uses a constant amount of extra space.
9. Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
- Simple and easy to understand and implement.
- No preprocessing required.
Disadvantages:
- Inefficient for large texts and patterns with many repeated characters.
- Higher time complexity compared to more advanced algorithms like Boyer-Moore and KMP.
10. References
- GFG Problem: GFG Problem
- HackerRank Problem: HackerRank
- Author's Geeks for Geeks Profile: GeeksforGeeks