Linear Search and Binary Search Algorithms
In this tutorial, we will delve into two fundamental search algorithms: linear search and binary search. We'll discuss their concepts, implementations, time complexities, and applications in different programming languages including Python, Java, C++, and JavaScript.
1. Linear Search
Linear search, also known as sequential search, is a simple search algorithm that checks every element in a list or array until the target element is found or the end of the list is reached. It is straightforward but may be inefficient for large datasets.

- Python
- Java
- Cpp
- JavaScript
def linear_search(arr, target):
for i in range(len(arr)):
if arr[i] == target:
return i
return -1
arr = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
target = 30
print(linear_search(arr, target)) # Output: 2
public class LinearSearch {
public static int linearSearch(int[] arr, int target) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] == target) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
int target = 30;
System.out.println(linearSearch(arr, target)); // Output: 2
}
}
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
int linearSearch(const std::vector<int>& arr, int target) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++) {
if (arr[i] == target) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
int main() {
std::vector<int> arr = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
int target = 30;
std::cout << linearSearch(arr, target) << std::endl; // Output: 2
return 0;
}
function linearSearch(arr, target) {
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] === target) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
let arr = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50];
let target = 30;
console.log(linearSearch(arr, target)); // Output: 2
2. Binary Search
Binary search is a more efficient search algorithm for sorted arrays. It works by repeatedly dividing the search interval in half until the target element is found or the interval is empty.
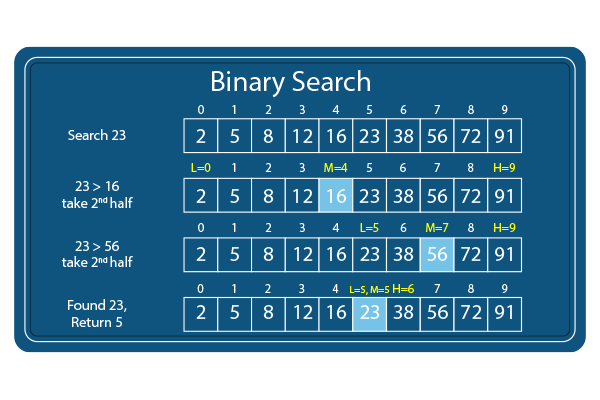
- Python
- Java
- Cpp
- JavaScript
def binary_search(arr, target):
low = 0
high = len(arr) - 1
while low <= high:
mid = (low + high) // 2
if arr[mid] == target:
return mid
elif arr[mid] < target:
low = mid + 1
else:
high = mid - 1
return -1
arr = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
target = 30
print(binary_search(arr, target)) # Output: 2
public class BinarySearch {
public static int binarySearch(int[] arr, int target) {
int low = 0;
int high = arr.length - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) / 2;
if (arr[mid] == target) {
return mid;
} else if (arr[mid] < target) {
low = mid + 1;
} else {
high = mid - 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
int target = 30;
System.out.println(binarySearch(arr, target)); // Output: 2
}
}
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
int binarySearch(const std::vector<int>& arr, int target) {
int low = 0;
int high = arr.size() - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) / 2;
if (arr[mid] == target) {
return mid;
} else if (arr[mid] < target) {
low = mid + 1;
} else {
high = mid - 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
int main() {
std::vector<int> arr = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
int target = 30;
std::cout << binarySearch(arr, target) << std::endl; // Output: 2
return 0;
}
function binarySearch(arr, target) {
let low = 0;
let high = arr.length - 1;
while (low <= high) {
let mid = Math.floor((low + high) / 2);
if (arr[mid] === target) {
return mid;
} else if (arr[mid] < target) {
low = mid + 1;
} else {
high = mid - 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
let arr = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50];
let target = 30;
console.log(binarySearch(arr, target)); // Output: 2
Time Complexity Analysis
- Linear Search:
- Best Case: (when the target is found at the first position)
- Worst Case: (when the target is not present in the array or at the last position)
- Binary Search:
- Best Case: (when the target is found at the middle position)
- Worst Case: (when the target is not present in the array or at the last position)
Applications of Linear Search and Binary Search
- Linear Search: Used in scenarios where the data is unsorted or small in size.
- Binary Search: Ideal for searching in large sorted datasets, such as searching in databases or sorted arrays.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we explored linear search and binary search algorithms along with their implementations in Python, Java, C++, and JavaScript. Understanding these fundamental search algorithms is essential for solving various problems efficiently.