1232. Check If It Is a Straight Line
Problem Description
You are given an array coordinates, coordinates[i] = [x, y], where [x, y] represents the coordinate of a point. Check if these points make a straight line in the XY plane.
Examples
Example 1:
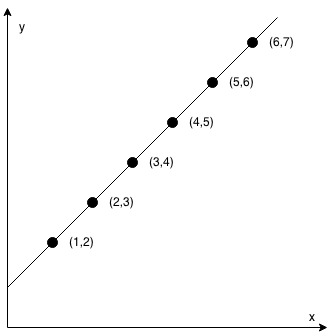
Input: coordinates = [[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[4,5],[5,6],[6,7]]
Output: true
Example 2:
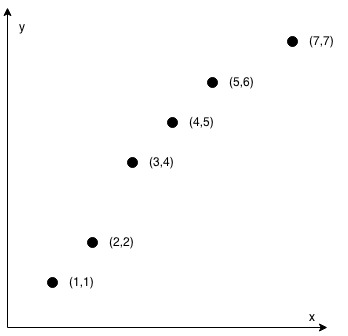
Input: coordinates = [[1,1],[2,2],[3,4],[4,5],[5,6],[7,7]]
Output: false
Constraints
2 <= coordinates.length <= 1000coordinates[i].length == 2-10^4 <= coordinates[i][0], coordinates[i][1] <= 10^4coordinates contains no duplicate point.
Solution for 1232. Check If It Is a Straight Line Problem
Approach
-
Calculate the Initial Slope:
- Compute the difference in the
yvalues (diff_y) and the difference in thexvalues (diff_x) between the first two points.
- Compute the difference in the
-
Iterate through the Points:
- For each subsequent point, compute the product of the initial slope differences with the current point's differences.
- If at any point the calculated products do not match, the points do not lie on a straight line.
-
Return the Result:
- If all points satisfy the condition, return
true. Otherwise, returnfalse.
- If all points satisfy the condition, return
- Solution
Implementation
Live Editor
function Solution(arr) { function checkStraightLine(coordinates) { const diff_y = (coordinates[1][1] - coordinates[0][1]); const diff_x = (coordinates[1][0] - coordinates[0][0]); for (let i = 2; i < coordinates.length; i++) { if (diff_y * (coordinates[i][0] - coordinates[i-1][0]) !== diff_x * (coordinates[i][1] - coordinates[i-1][1])) { return false; } } return true; } const input = [[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[4,5],[5,6],[6,7]] const output = checkStraightLine(input) return ( <div> <p> <b>Input: </b> {JSON.stringify(input)} </p> <p> <b>Output:</b> {output.toString()} </p> </div> ); }
Result
Loading...
Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity:
- Space Complexity:
Code in Different Languages
- JavaScript
- TypeScript
- Python
- Java
- C++
function checkStraightLine(coordinates) {
const diff_y = (coordinates[1][1] - coordinates[0][1]);
const diff_x = (coordinates[1][0] - coordinates[0][0]);
for (let i = 2; i < coordinates.length; i++) {
if (diff_y * (coordinates[i][0] - coordinates[i-1][0]) !== diff_x * (coordinates[i][1] - coordinates[i-1][1])) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
class Solution {
checkStraightLine(coordinates: number[][]): boolean {
const diff_y = (coordinates[1][1] - coordinates[0][1]);
const diff_x = (coordinates[1][0] - coordinates[0][0]);
for (let i = 2; i < coordinates.length; i++) {
if (diff_y * (coordinates[i][0] - coordinates[i-1][0]) !== diff_x * (coordinates[i][1] - coordinates[i-1][1])) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
class Solution:
def checkStraightLine(self, coordinates: List[List[int]]) -> bool:
diff_y = (coordinates[1][1] - coordinates[0][1])
diff_x = (coordinates[1][0] - coordinates[0][0])
for i in range(2, len(coordinates)):
if diff_y * (coordinates[i][0] - coordinates[i-1][0]) != diff_x * (coordinates[i][1] - coordinates[i-1][1]):
return False
return True
import java.util.List;
class Solution {
public boolean checkStraightLine(List<int[]> coordinates) {
int diff_y = (coordinates.get(1)[1] - coordinates.get(0)[1]);
int diff_x = (coordinates.get(1)[0] - coordinates.get(0)[0]);
for (int i = 2; i < coordinates.size(); i++) {
if (diff_y * (coordinates.get(i)[0] - coordinates.get(i-1)[0]) != diff_x * (coordinates.get(i)[1] - coordinates.get(i-1)[1])) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
class Solution {
public:
bool checkStraightLine(vector<vector<int>>& coordinates) {
int diff_y = (coordinates[1][1] - coordinates[0][1]);
int diff_x = (coordinates[1][0] - coordinates[0][0]);
for(int i=2; i<coordinates.size(); i++)
{
if(diff_y*(coordinates[i][0] - coordinates[i-1][0]) != diff_x*(coordinates[i][1] - coordinates[i-1][1]))
return false;
}
return true;
}
};
References
-
LeetCode Problem: Check If It Is a Straight Line
-
Solution Link: LeetCode Solution