2096. Step-By-Step Directions From a Binary Tree Node to Another
Problem Description
You are given the root of a binary tree with n nodes. Each node is uniquely assigned a value from 1 to n. You are also given an integer startValue representing the value of the start node s, and a different integer destValue representing the value of the destination node t.
Find the shortest path starting from node s and ending at node t. Generate step-by-step directions of such path as a string consisting of only the uppercase letters 'L', 'R', and 'U'. Each letter indicates a specific direction:
'L' means to go from a node to its left child node. 'R' means to go from a node to its right child node. 'U' means to go from a node to its parent node. Return the step-by-step directions of the shortest path from node s to node t.
Examples
Example 1:
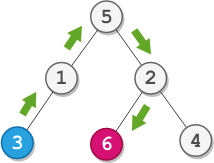
Input: root = [5,1,2,3,null,6,4], startValue = 3, destValue = 6
Output: "UURL"
Explanation: The shortest path is: 3 → 1 → 5 → 2 → 6.
Constraints
The number of nodes in the tree is n.2 <= n <= 10^51 <= Node.val <= nAll the values in the tree are unique.1 <= startValue, destValue <= nstartValue != destValue
Solution for 2096. Step-By-Step Directions From a Binary Tree Node to Another
- Solution
Implementation
function Solution(arr) { class TreeNode { constructor(val = 0, left = null, right = null) { this.val = val; this.left = left; this.right = right; } } class Solve { constructor() { this.path1 = ""; this.path2 = ""; } solve(root, node, temp, st) { if (!root) return; if (root.val === node) { if (st === 1) this.path1 = temp; else this.path2 = temp; return; } temp += 'L'; this.solve(root.left, node, temp, st); temp = temp.slice(0, -1); temp += 'R'; this.solve(root.right, node, temp, st); temp = temp.slice(0, -1); } getDirections(root, startValue, destValue) { let temp = ""; this.solve(root, startValue, temp, 1); temp = ""; this.solve(root, destValue, temp, 0); let i = 0; while (i < this.path1.length && i < this.path2.length && this.path1[i] === this.path2[i]) { i++; } let result = ""; for (let j = i; j < this.path1.length; j++) { result += 'U'; } result += this.path2.substring(i); return result; } } const input =0 const output = 0 return ( <div> <p> <b>Input: </b> {JSON.stringify(input)} </p> <p> <b>Output:</b> {output.toString()} </p> </div> ); }
Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity:
- Space Complexity:
Code in Different Languages
- Python
- Java
- C++
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.path1 = ""
self.path2 = ""
def solve(self, root, node, temp, st):
if not root:
return
if root.val == node:
if st == 1:
self.path1 = temp
else:
self.path2 = temp
return
self.solve(root.left, node, temp + 'L', st)
self.solve(root.right, node, temp + 'R', st)
def getDirections(self, root, startValue, destValue):
self.solve(root, startValue, "", 1)
self.solve(root, destValue, "", 0)
i = 0
while i < len(self.path1) and i < len(self.path2) and self.path1[i] == self.path2[i]:
i += 1
result = 'U' * (len(self.path1) - i) + self.path2[i:]
return result
class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
}
public class Solution {
String path1 = "";
String path2 = "";
void solve(TreeNode root, int node, StringBuilder temp, int st) {
if (root == null) return;
if (root.val == node) {
if (st == 1) path1 = temp.toString();
else path2 = temp.toString();
return;
}
temp.append('L');
solve(root.left, node, temp, st);
temp.deleteCharAt(temp.length() - 1);
temp.append('R');
solve(root.right, node, temp, st);
temp.deleteCharAt(temp.length() - 1);
}
public String getDirections(TreeNode root, int startValue, int destValue) {
StringBuilder temp = new StringBuilder();
solve(root, startValue, temp, 1);
temp = new StringBuilder();
solve(root, destValue, temp, 0);
int i = 0;
while (i < path1.length() && i < path2.length() && path1.charAt(i) == path2.charAt(i)) {
i++;
}
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
for (int j = i; j < path1.length(); j++) {
result.append('U');
}
result.append(path2.substring(i));
return result.toString();
}
}
class Solution {
public:
string path1 = "";
string path2 = "";
void solve(TreeNode* root, int node, string &temp, int st) {
if (!root) return ;
if (root->val == node) {
if (st == 1) path1 = temp;
else path2 = temp;
return ;
}
temp.push_back('L');
solve(root->left, node, temp, st);
temp.pop_back();
temp.push_back('R');
solve(root->right, node, temp, st);
temp.pop_back();
}
string getDirections(TreeNode* root, int startValue, int destValue) {
string temp = "";
solve(root, startValue, temp, 1);
temp = "";
solve(root, destValue, temp, 0);
cout << path1 <<" "<<path2;
int i = 0;
while (i < path1.length() && i < path2.length() && path1[i] == path2[i]) {
i++;
}
string result = "";
for (int j = i; j < path1.length(); j++) {
result += 'U';
}
result += path2.substr(i);
return result;
}
};
References
-
LeetCode Problem: 2096. Step-By-Step Directions From a Binary Tree Node to Another
-
Solution Link: LeetCode Solution