Introduction to Spring
This spring tutorial provides in-depth concepts of the Spring Framework with simplified examples. It was developed by Rod Johnson in 2003. The Spring framework makes the easy development of JavaEE applications.
It is helpful for beginners and experienced persons.

Why Learn Spring?
Spring is the most popular application development framework for enterprise Java. Millions of developers around the world use the Spring Framework to create high-performing, easily testable, and reusable code.
Spring framework is an open-source Java platform. It was initially written by Rod Johnson and was first released under the Apache 2.0 license in June 2003.
Spring is lightweight when it comes to size and transparency. The basic version of the Spring framework is around 2MB.
The core features of the Spring Framework can be used in developing any Java application, but there are extensions for building web applications on top of the Java EE platform. The Spring framework aims to make J2EE development easier to use and promotes good programming practices by enabling a POJO-based programming model.
Spring Framework
Spring is a lightweight framework. It can be thought of as a framework of frameworks because it provides support to various frameworks such as Struts, Hibernate, Tapestry, EJB, JSF, etc. The framework, in a broader sense, can be defined as a structure where we find solutions to various technical problems.
The Spring framework comprises several modules such as IOC, AOP, DAO, Context, ORM, WEB MVC, etc. We will learn these modules on the next page. Let's understand the IOC and Dependency Injection first.
Advantages of Spring Framework
There are many advantages of the Spring Framework. They are as follows:
-
Predefined Templates: Spring framework provides templates for JDBC, Hibernate, JPA, etc. technologies. So there is no need to write too much code. It hides the basic steps of these technologies. For example, with JdbcTemplate, you don't need to write code for exception handling, creating connections, creating statements, committing transactions, closing connections, etc. You only need to write the code for executing queries. Thus, it saves a lot of JDBC code.
-
Loose Coupling: Spring applications are loosely coupled because of dependency injection.
-
Easy to Test: Dependency Injection makes it easier to test applications. EJB or Struts applications require a server to run, but the Spring framework doesn't require a server.
-
Lightweight: The Spring framework is lightweight because of its POJO implementation. The Spring Framework doesn't force the programmer to inherit any class or implement any interface, making it non-invasive.
-
Fast Development: The Dependency Injection feature of the Spring Framework and its support for various frameworks make JavaEE application development easy.
-
Powerful Abstraction: It provides powerful abstraction to JavaEE specifications such as JMS, JDBC, JPA, and JTA.
-
Declarative Support:
Applications of Spring
The benefits of using the Spring Framework include:
-
POJO Based: Spring enables developers to develop enterprise-class applications using POJOs. This means you do not need an EJB container product such as an application server; you can use a robust servlet container such as Tomcat.
-
Modular: Spring is organized in a modular fashion. Although there are many packages and classes, you only need to worry about the ones you need.
-
Integration with Existing Frameworks: Spring does not reinvent the wheel; it uses existing technologies like ORM frameworks, logging frameworks, JEE, Quartz, JDK timers, and other view technologies.
-
Testability: Testing a Spring application is simple because environment-dependent code is moved into this framework. Using JavaBean-style POJOs makes it easier to use dependency injection for injecting test data.
-
Web MVC: Spring's web framework is a well-designed web MVC framework, providing a great alternative to web frameworks like Struts.
-
Central Exception Handling: Spring provides a convenient API to translate technology-specific exceptions (e.g., JDBC, Hibernate, JDO) into consistent, unchecked exceptions.
-
Lightweight: Lightweight IoC containers are beneficial for developing and deploying applications on computers with limited memory and CPU resources.
-
Transaction Management: Spring provides a consistent transaction management interface that can scale from local to global transactions.
Spring Modules
The Spring framework comprises many modules such as core, beans, context, expression language, AOP, Aspects, Instrumentation, JDBC, ORM, OXM, JMS, Transaction, Web, Servlet, Struts, etc. These modules are grouped into Test, Core Container, AOP, Aspects, Instrumentation, Data Access/Integration, and Web (MVC/Remoting).
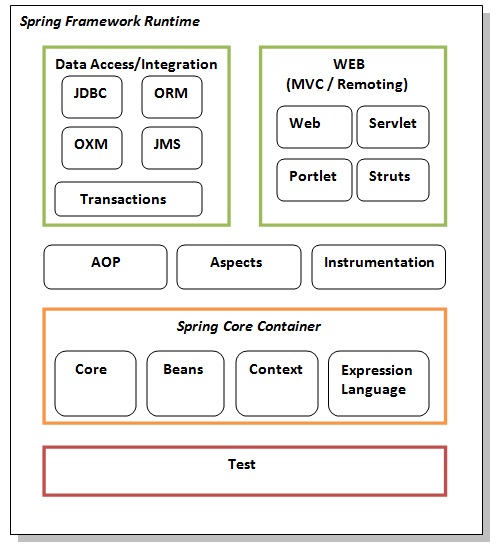
Test
This layer provides support for testing with JUnit and TestNG.
Spring Core Container
The Spring Core container contains core, beans, context, and expression language (EL) modules.
Core and Beans
These modules provide IOC and Dependency Injection features.
Context
This module supports internationalization (I18N), EJB, JMS, and Basic Remoting.
Expression Language
It is an extension to the EL defined in JSP. It provides support for setting and getting property values, method invocation, accessing collections and indexers, named variables, logical and arithmetic operators, retrieval of objects by name, etc.
AOP, Aspects, and Instrumentation
These modules support aspect-oriented programming implementation where you can use Advices, Pointcuts, etc., to decouple the code.
The Aspects module provides support for integration with AspectJ.
The Instrumentation module provides support for class instrumentation and classloader implementations.
Data Access/Integration
This group comprises JDBC, ORM, OXM, JMS, and Transaction modules. These modules provide support for interacting with databases.
Web
This group comprises Web, Web-Servlet, Web-Struts, and Web-Portlet modules. These modules provide support for creating web applications. Sure! Here’s a conclusion section for the Spring tutorial:
Conclusion
The Spring Framework is a powerful, versatile, and comprehensive platform for developing Java applications. Its modular architecture allows developers to focus on specific aspects of application development without being bogged down by unnecessary complexity. The benefits of using Spring, such as its lightweight nature, robust transaction management, and ease of integration with other technologies, make it an excellent choice for both beginners and experienced developers.
By leveraging Spring's core features, like dependency injection and aspect-oriented programming, developers can create maintainable, testable, and high-performing applications. Whether you're building a simple web application or a complex enterprise system, Spring provides the tools and frameworks necessary to streamline development and promote best practices.
As you continue to explore and learn more about Spring, you'll discover how its flexibility and extensive ecosystem can help you tackle a wide range of development challenges efficiently.