Find All Groups of Farmland
Problem Description
You are given a 0-indexed m x n binary matrix land where a 0 represents a hectare of forested land and a 1 represents a hectare of farmland.
To keep the land organized, there are designated rectangular areas of hectares that consist entirely of farmland. These rectangular areas are called groups. No two groups are adjacent, meaning farmland in one group is not four-directionally adjacent to another farmland in a different group.
land can be represented by a coordinate system where the top left corner of land is (0, 0) and the bottom right corner of land is (m-1, n-1). Find the coordinates of the top left and bottom right corner of each group of farmland. A group of farmland with a top left corner at (r1, c1) and a bottom right corner at (r2, c2) is represented by the 4-length array [r1, c1, r2, c2].
Return a 2D array containing the 4-length arrays described above for each group of farmland in land. If there are no groups of farmland, return an empty array. You may return the answer in any order.
Examples
Example 1:
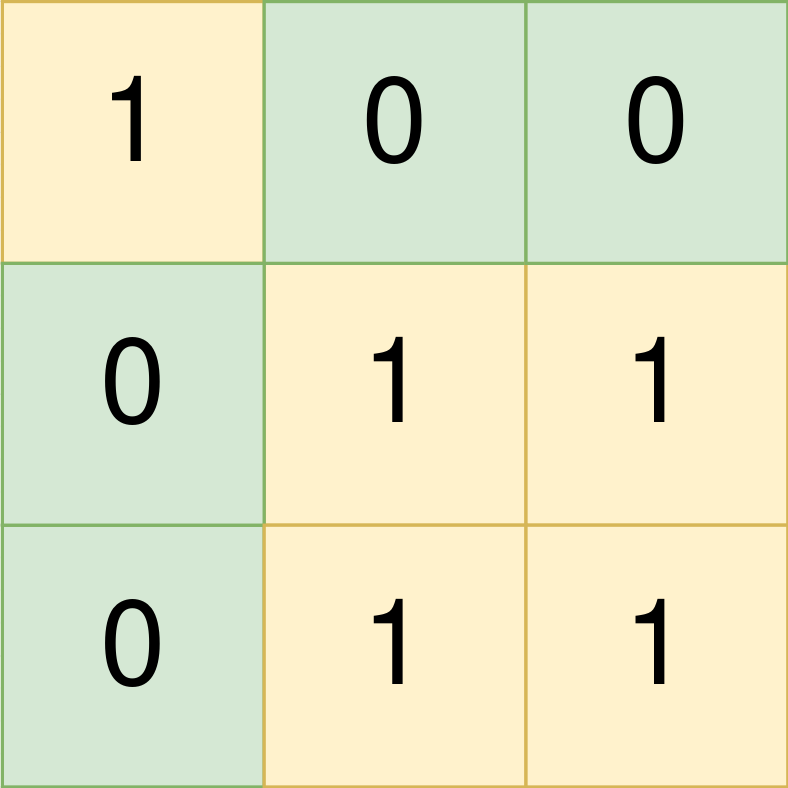
Input: land = [[1,0,0],[0,1,1],[0,1,1]]
Output: [[0,0,0,0],[1,1,2,2]]
Example 2:
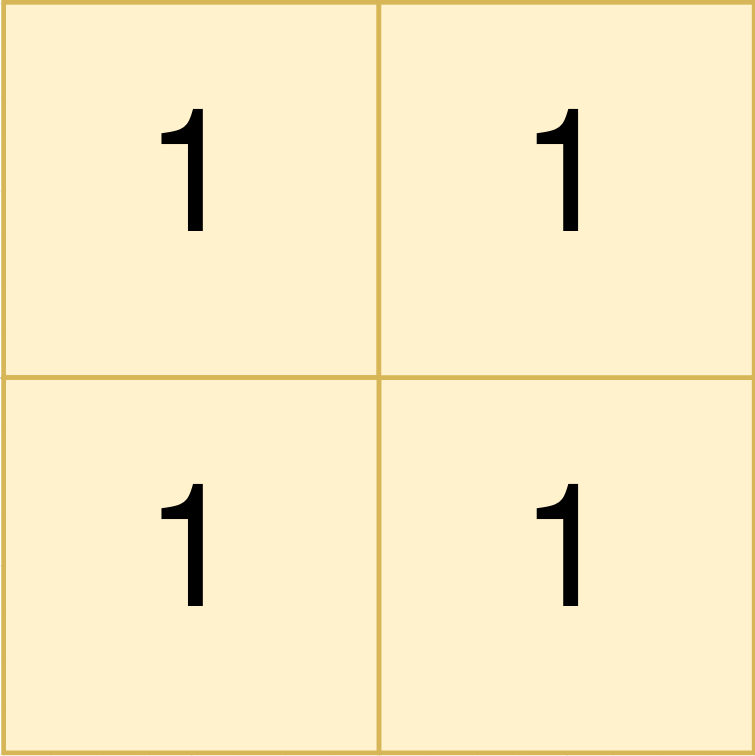
Input: land = [[1,1],[1,1]]
Output: [[0,0,1,1]]
Explanation:
The first group has a top left corner at land[0][0] and a bottom right corner at land[1][1].
Constraints
m == land.lengthn == land[i].length1 <= m, n <= 300- land consists of only 0's and 1's.
- Groups of farmland are rectangular in shape.
Solution for Remove Stones to Minimize the Total Problem
Intuition
The problem is to find all the rectangular farmlands in a grid. Each cell in the grid is either part of a farmland (denoted by 1) or not (denoted by 0). Farmlands are connected horizontally or vertically and form rectangular shapes. The goal is to identify the top-left and bottom-right coordinates of each rectangular farmland.
Approach
-
Grid Traversal:
- Traverse each cell in the grid.
- When encountering a cell with a value of 1 (indicating the start of a new farmland), initiate a Breadth-First Search (BFS) to find the extent of this farmland.
-
Breadth-First Search (BFS):
- Use a queue to explore all cells connected to the current farmland.
- Track the maximum row and column indices (
eRandeC) to determine the bottom-right corner of the farmland. - For each cell, check its four neighboring cells (up, down, left, right). If a neighboring cell is part of the farmland (i.e., its value is 1), add it to the queue and mark it as visited (set its value to 0).
-
Record Farmland:
- After completing the BFS for a farmland, record its top-left and bottom-right coordinates.
- Continue the grid traversal to find all farmlands.
- Solution
Implementation
function Solution(arr) { function findFarmland(land) { const ans = []; const m = land.length; const n = land[0].length; const delRow = [-1, 0, 1, 0]; const delCol = [0, 1, 0, -1]; const q = []; for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) { for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) { if (land[i][j] === 1) { q.push([i, j]); land[i][j] = 0; let eR = i, eC = j; while (q.length > 0) { const [sR, sC] = q.shift(); for (let k = 0; k < 4; k++) { const nR = sR + delRow[k]; const nC = sC + delCol[k]; if (nR >= 0 && nR < m && nC >= 0 && nC < n && land[nR][nC] === 1) { q.push([nR, nC]); land[nR][nC] = 0; eR = Math.max(eR, nR); eC = Math.max(eC, nC); } } } ans.push([i, j, eR, eC]); } } } return ans; } const input = [[1,0,0],[0,1,1],[0,1,1]] const output =findFarmland(input) return ( <div> <p> <b>Input: </b> {JSON.stringify(input)} </p> <p> <b>Output:</b> {output.toString()} </p> </div> ); }
Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity:
- Space Complexity:
Code in Different Languages
- JavaScript
- TypeScript
- Python
- Java
- C++
function findFarmland(land) {
const ans = [];
const m = land.length;
const n = land[0].length;
const delRow = [-1, 0, 1, 0];
const delCol = [0, 1, 0, -1];
const q = [];
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (land[i][j] === 1) {
q.push([i, j]);
land[i][j] = 0;
let eR = i, eC = j;
while (q.length > 0) {
const [sR, sC] = q.shift();
for (let k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
const nR = sR + delRow[k];
const nC = sC + delCol[k];
if (nR >= 0 && nR < m && nC >= 0 && nC < n && land[nR][nC] === 1) {
q.push([nR, nC]);
land[nR][nC] = 0;
eR = Math.max(eR, nR);
eC = Math.max(eC, nC);
}
}
}
ans.push([i, j, eR, eC]);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
function findFarmland(land: number[][]): number[][] {
const ans: number[][] = [];
const m = land.length;
const n = land[0].length;
const delRow = [-1, 0, 1, 0];
const delCol = [0, 1, 0, -1];
const q: [number, number][] = [];
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (land[i][j] === 1) {
q.push([i, j]);
land[i][j] = 0;
let eR = i, eC = j;
while (q.length > 0) {
const [sR, sC] = q.shift()!;
for (let k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
const nR = sR + delRow[k];
const nC = sC + delCol[k];
if (nR >= 0 && nR < m && nC >= 0 && nC < n && land[nR][nC] === 1) {
q.push([nR, nC]);
land[nR][nC] = 0;
eR = Math.max(eR, nR);
eC = Math.max(eC, nC);
}
}
}
ans.push([i, j, eR, eC]);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
from collections import deque
class Solution:
def findFarmland(self, land: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
ans = []
m, n = len(land), len(land[0])
delRow = [-1, 0, 1, 0]
delCol = [0, 1, 0, -1]
q = deque()
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
if land[i][j] == 1:
q.append((i, j))
land[i][j] = 0
eR, eC = i, j
while q:
sR, sC = q.popleft()
for k in range(4):
nR, nC = sR + delRow[k], sC + delCol[k]
if 0 <= nR < m and 0 <= nC < n and land[nR][nC] == 1:
q.append((nR, nC))
land[nR][nC] = 0
eR = max(eR, nR)
eC = max(eC, nC)
ans.append([i, j, eR, eC])
return ans
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public List<int[]> findFarmland(int[][] land) {
List<int[]> ans = new ArrayList<>();
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
int m = land.length;
int n = land[0].length;
int[] delRow = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
int[] delCol = {0, 1, 0, -1};
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (land[i][j] == 1) {
q.add(new int[]{i, j});
land[i][j] = 0;
int eR = i, eC = j;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] cell = q.poll();
int sR = cell[0];
int sC = cell[1];
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int nR = sR + delRow[k];
int nC = sC + delCol[k];
if (nR >= 0 && nR < m && nC >= 0 && nC < n && land[nR][nC] == 1) {
q.add(new int[]{nR, nC});
land[nR][nC] = 0;
eR = Math.max(eR, nR);
eC = Math.max(eC, nC);
}
}
}
ans.add(new int[]{i, j, eR, eC});
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> findFarmland(vector<vector<int>>& land) {
vector<vector<int>> ans;
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
int m = land.size();
int n = land[0].size();
int delRow[4] = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
int delCol[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (land[i][j] == 1) {
q.push({i, j});
land[i][j] = 0;
int eR = i, eC = j;
while (!q.empty()) {
int sR = q.front().first;
int sC = q.front().second;
q.pop();
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int nR = sR + delRow[k];
int nC = sC + delCol[k];
if (nR >= 0 && nR < m && nC >= 0 && nC < n && land[nR][nC] == 1) {
q.push({nR, nC});
land[nR][nC] = 0;
eR = max(eR, nR);
eC = max(eC, nC);
}
}
}
ans.push_back({i, j, eR, eC});
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};
References
-
LeetCode Problem: Find All Groups of Farmland
-
Solution Link: LeetCode Solution