Heaps Data Structure
Python - Heaps
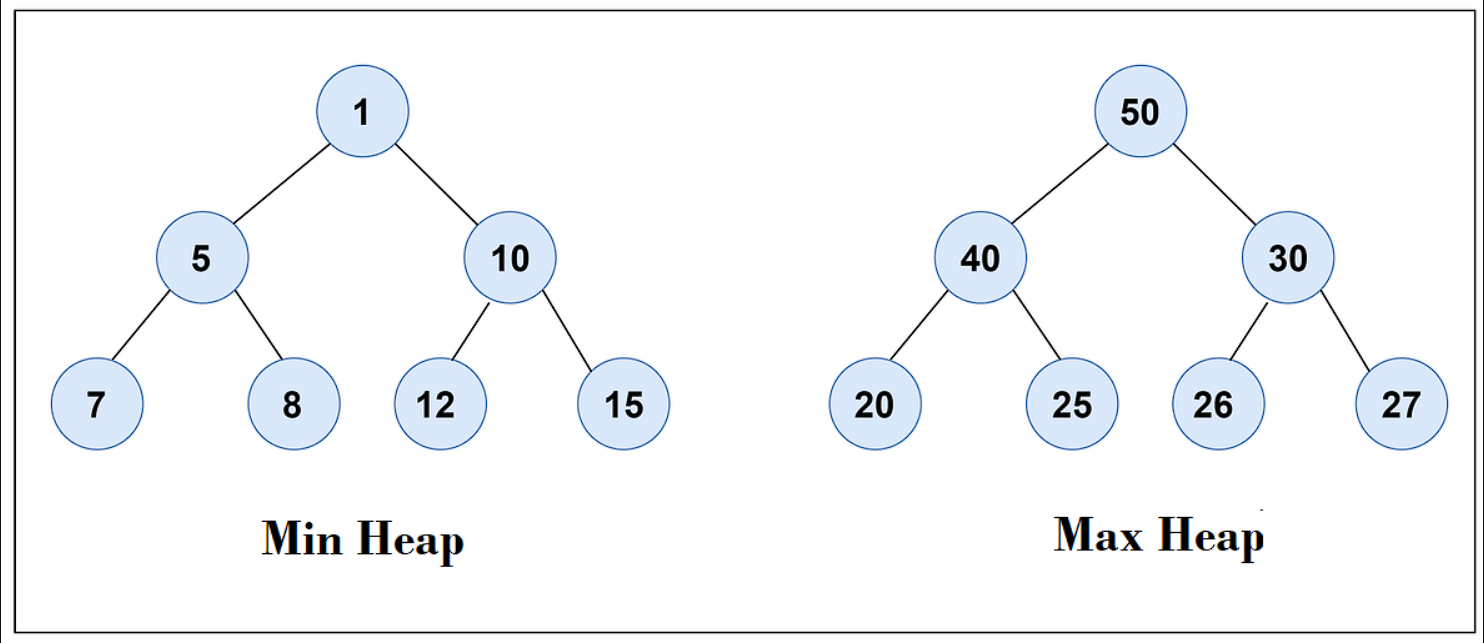
Heap is a special tree structure in which each parent node is less than or equal to its child node. Then it is called a Min Heap. If each parent node is greater than or equal to its child node then it is called a max heap. It is very useful is implementing priority queues where the queue item with higher weightage is given more priority in processing.
A detailed discussion on heaps is available in our website here. Please study it first if you are new to heap data structure. In this chapter we will see the implementation of heap data structure using python.
Create a Heap
A heap is created by using python’s inbuilt library named heapq. This library has the relevant functions to carry out various operations on heap data structure. Below is a list of these functions.
-
heapify − This function converts a regular list to a heap. In the resulting heap the smallest element gets pushed to the index position 0. But rest of the data elements are not necessarily sorted.
-
heappush − This function adds an element to the heap without altering the current heap.
-
heappop − This function returns the smallest data element from the heap.
-
heapreplace − This function replaces the smallest data element with a new value supplied in the function.
Creating a Heap
A heap is created by simply using a list of elements with the heapify function. In the below example we supply a list of elements and the heapify function rearranges the elements bringing the smallest element to the first position.
Python - Heaps
Heap is a special tree structure in which each parent node is less than or equal to its child node. Then it is called a Min Heap.
If each parent node is greater than or equal to its child node then it is called a max heap.
It is very useful is implementing priority queues where the queue item with higher weightage is given more priority in processing.
A detailed discussion on heaps is available in our website here. Please study it first if you are new to heap data structure. In this chapter we will see the implementation of heap data structure using python.
Example
import heapq
H = [21,1,45,78,3,5]
# Use heapify to rearrange the elements
heapq.heapify(H)
print(H)
Output
When the above code is executed, it produces the following result −
[1, 3, 5, 78, 21, 45]
Inserting into heap
Inserting a data element to a heap always adds the element at the last index. But you can apply heapify function again to bring the newly added element to the first index only if it smallest in value. In the below example we insert the number 8.
Example
import heapq
H = [21,1,45,78,3,5]
# Covert to a heap
heapq.heapify(H)
print(H)
# Add element
heapq.heappush(H,8)
print(H)
Output
When the above code is executed, it produces the following result −
[1, 3, 5, 78, 21, 45]
[1, 3, 5, 78, 21, 45, 8]
Removing from heap
You can remove the element at first index by using this function. In the below example the function will always remove the element at the index position 1.
Example
import heapq
H = [21,1,45,78,3,5]
# Create the heap
heapq.heapify(H)
print(H)
# Remove element from the heap
heapq.heappop(H)
print(H)
Output
When the above code is executed, it produces the following result −
```python
[1, 3, 5, 78, 21, 45]
[3, 21, 5, 78, 45]
Replacing in a Heap
The heap replace function always removes the smallest element of the heap and inserts the new incoming element at some place not fixed by any order.
Example
import heapq
H = [21,1,45,78,3,5]
# Create the heap
heapq.heapify(H)
print(H)
# Replace an element
heapq.heapreplace(H,6)
print(H)
Output
When the above code is executed, it produces the following result −
[1, 3, 5, 78, 21, 45]
[3, 6, 5, 78, 21, 45]